Overview
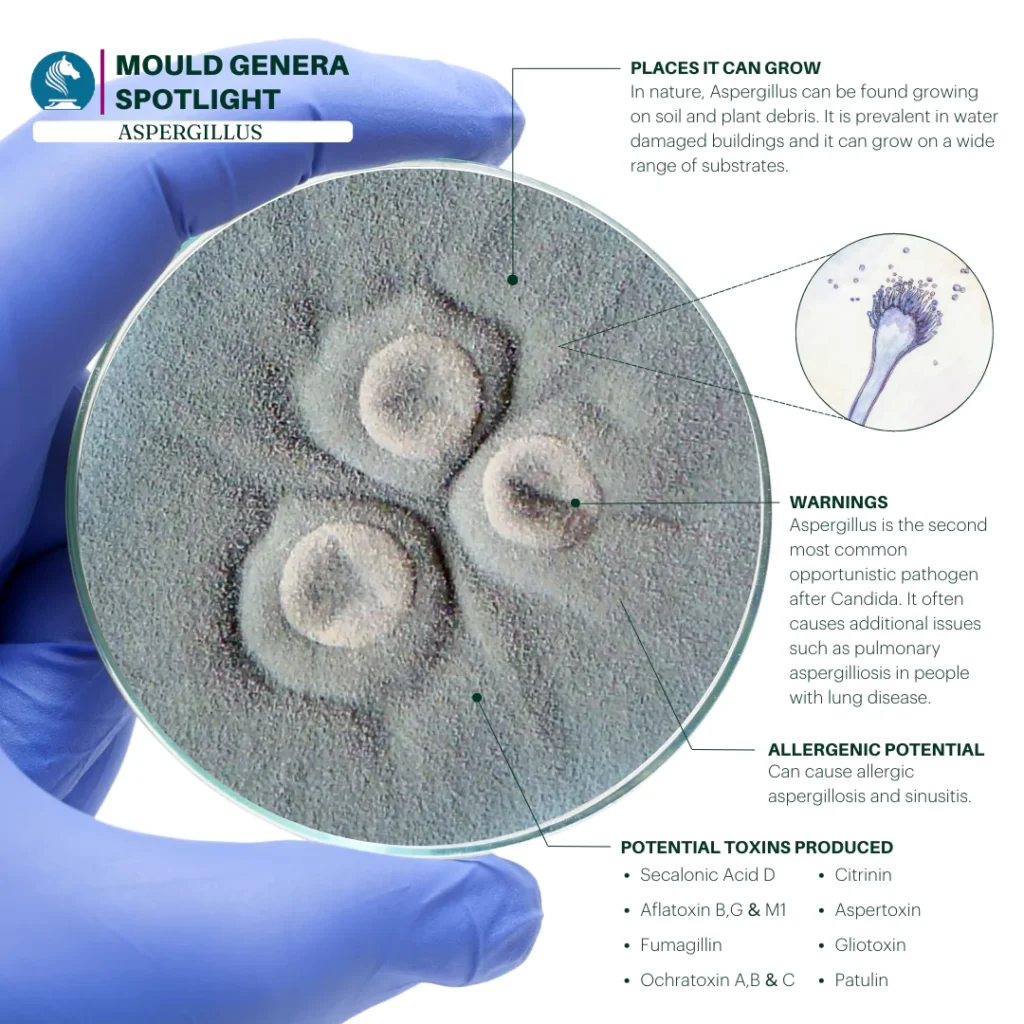
Aspergillus is one of the most common and diverse genera of moulds, with hundreds of species found in various environments worldwide. Some of the most well-known species include Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger, and Aspergillus flavus. While it plays a vital role in ecosystems by decomposing organic matter, Aspergillus can also pose significant health risks and is known for producing harmful mycotoxins.
Habitat and Growth Locations
Aspergillus thrives in a variety of environments:
- Indoor areas: It can grow in damp homes, particularly on walls, ceilings, insulation, and HVAC systems. It thrives in warm, humid conditions, especially after water damage.
- Outdoor environments: It is frequently found in soil, decaying vegetation, and compost piles, where it breaks down organic matter.
- Food products: Aspergillus is known to contaminate stored grains, spices, nuts, and other food items, making it a concern for food safety.
- Construction materials: It can colonise building materials such as plasterboard and wood, especially after flooding or leaks.
Health Risks and Allergenic Potential
Several species of Aspergillus are known for causing health problems, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions:
- Allergic reactions: Inhalation of Aspergillus spores can cause allergic symptoms, including sneezing, coughing, itchy eyes, and congestion. It is a common cause of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), particularly in people with asthma or cystic fibrosis.
- Aspergillosis: Certain species like Aspergillus fumigatus can cause a range of infections collectively known as aspergillosis. This can include:
- Allergic aspergillosis, affecting the lungs.
- Invasive aspergillosis, a life-threatening infection in immunocompromised individuals, where the mould invades lung tissue or other organs.
- Respiratory issues: Prolonged exposure to airborne spores can exacerbate asthma and lead to other chronic respiratory problems, especially in damp indoor environments.
Toxins Produced
Many Aspergillus species are known for producing dangerous mycotoxins, which can contaminate both air and food:
- Aflatoxins: Produced mainly by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus, aflatoxins are among the most potent natural carcinogens and can contaminate foods such as peanuts, corn, and grains.
- Ochratoxin A: Aspergillus niger and other species can produce this toxin, which affects kidney function and has been linked to cancer.
- Gliotoxins: Found in species like Aspergillus fumigatus, these toxins can suppress the immune system, making infections more difficult to combat.
These toxins are particularly dangerous in food storage, but even in the home, prolonged exposure to airborne spores and mycotoxins can affect health.
Industrial Uses
Despite its potential dangers, Aspergillus has a variety of industrial applications:
- Fermentation and biotechnology: Aspergillus niger is used to produce citric acid, a common ingredient in food and beverages. It also produces enzymes used in the fermentation of alcohol, detergents, and food processing.
- Pharmaceuticals: Certain species of Aspergillus are used in the production of antibiotics, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and other pharmaceuticals.
- Bioremediation: Aspergillus species can degrade various environmental pollutants, making them useful in cleaning up contaminated soils.